Fragments
Shattered Pieces
Fragments
Fragments are self-contained, reusable components in Android that represent a portion of a user interface within an activity. They enable dynamic and flexible UI designs, allowing developers to create versatile layouts that can adapt to different screen sizes and orientations. Fragments can be added, removed, or replaced within an activity at runtime, making it easy to create multi-pane interfaces, especially in tablet apps. They also manage their own lifecycle and can communicate with the parent activity, promoting the organization of code and improving the overall architecture of Android applications. By using fragments, developers can enhance user experience and maintain a cleaner code structure.
To Download Our Brochure: https://www.justacademy.co/download-brochure-for-free
Message us for more information: +91 9987184296
1 - Definition of Fragments: A fragment is a reusable portion of a user interface in an application, which can be combined with activities or other fragments to create a multi pane UI.
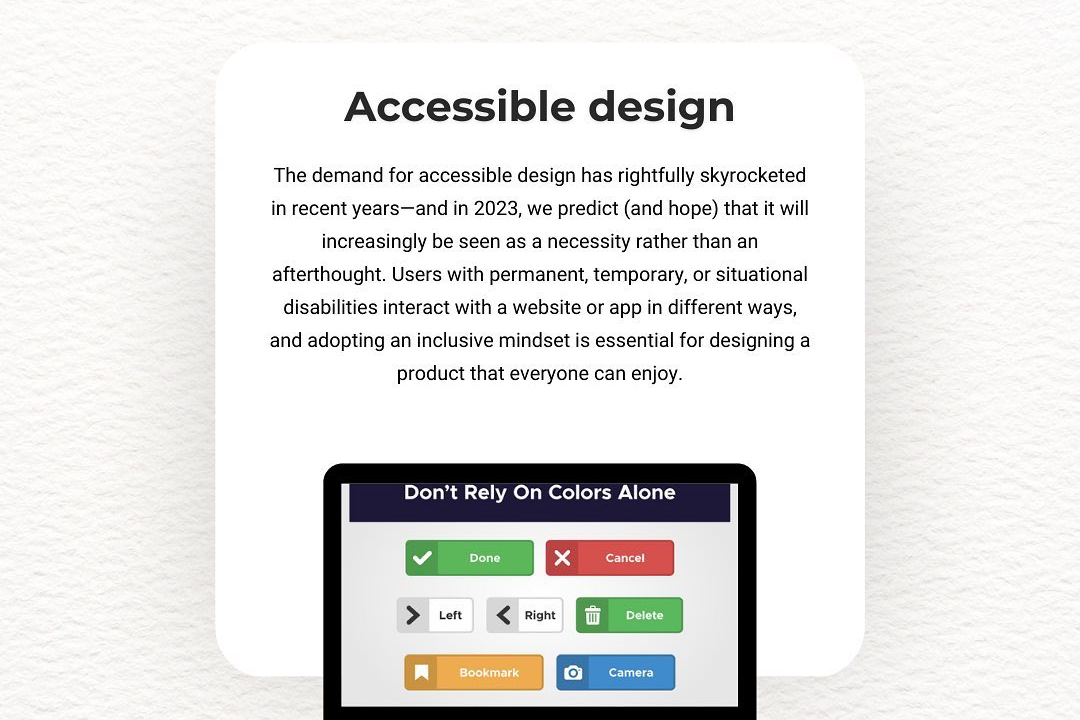
2) Modularity: Fragments help achieve modularity in application design, allowing developers to separate different UI components into manageable units for better readability and maintenance.
3) Lifecycle Management: Fragments have their own lifecycle, similar to activities. Understanding the lifecycle (onAttach, onCreate, onCreateView, etc.) is crucial for managing UI and resources properly.
4) Reusability: Fragments can be reused across different activities. This promotes code reuse and reduces redundancy, making it easier to update the UI.
5) Dynamic UI: Fragments enable developers to create dynamic and flexible UIs that can adapt to different screen sizes and orientations, which is beneficial for mobile applications.
6) Inter fragment Communication: Fragments can communicate with their parent activity and other fragments, allowing for coordinated behavior and shared data when needed.
7) Back Stack Support: Fragments can be added to the back stack managed by the activity, allowing users to navigate backward within the fragment transitions, similar to traditional activities.
8) UI Layouts: Fragments can be used to create multiple layouts for different screen sizes or orientations, thus facilitating the development of responsive designs.
9) State Preservation: Fragments can save their instance state, enabling them to restore their UI state when an activity is recreated, such as during configuration changes like screen rotations.
10) Fragment Transactions: The FragmentManager is responsible for handling fragment transactions, including adding, removing, and replacing fragments within an activity.
11) Argument Passing: Fragments can accept arguments through bundle objects, allowing the passing of data back and forth between the activity and fragments.
12) Nested Fragments: Fragments can contain other fragments, known as nested fragments, allowing for complex UI hierarchies and more modular designs.
13) View Binding: Fragments can use view binding techniques to interact with their views efficiently, thus minimizing boilerplate code and potential null pointer exceptions.
14) Testing: Fragments can be tested independently from their parent activity, facilitating unit testing and improving overall application quality.
15) Compatibility: The Fragment API exists in both the Android framework and the Android support library, ensuring compatibility across a wide range of devices and Android versions.
16) Use with ViewModels: Fragments can be designed to work alongside ViewModels from the Android Architecture Components, which help in managing UI related data lifecycle consciously.
17) Handling Configuration Changes: Fragments can help manage configuration changes like screen orientation or multi window mode better, as their state can be preserved independently of the containing activity.
18) Fragment Lifecycle Callbacks: Understanding fragment lifecycle callbacks is vital for managing resources. For instance, onActivityCreated is a place where you can initialize UI components after the activity’s onCreate has completed.
By offering training programs based on these points, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of fragments and their role in modern application development, especially in environments that support modular UI components.
Browse our course links : https://www.justacademy.co/all-courses
To Join our FREE DEMO Session: Click Here
Contact Us for more info:
best data analytics courses in india
Dark Mode Implementation
java full stack development course
Top 10 software training institute in pune
FLUTTER TRAINING in Siliguri